ADDITIONAL CORTICAL CONFLICTS
When a Temporal Lobes Constellation (Postmortal Constellation, Casanova Constellation, Nympho Constellation, Aggressive Constellation, Flying Constellation, Mytho Constellation, Autistic Constellation, Marking Constellation) has already been established, further conflicts, including conflicts related to the pre-motor sensory cortex (thyroid ducts and pharyngeal ducts relays) and glucose center, follow the Scale Rule. Whether additional conflicts register on the right or left brain hemisphere is determined by a person’s biological handedness and which one of the two conflicts is stronger at the time when the new conflicts occur.
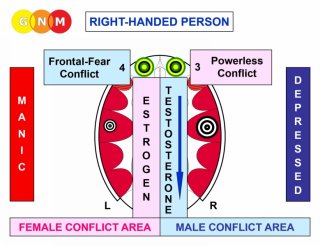
TEMPORAL LOBES - Right-Handers
|
| When a right-handed person (male or female) is in constellation, for example in an Aggressive Constellation, and the depression-related conflict (right temporal lobe) is accentuated, the third conflict registers also in the right cortical hemisphere. As a result, the depressive mood deepens. The same principle applies to further conflicts.
|
|
| When a right-handed person (male or female) is in an Aggressive Constellation and the mania-related conflict (left temporal lobe) is accentuated, the third conflict goes also to the left cortical hemisphere. As a result, the manic mood increases. The same principle applies to further conflicts.
|
TEMPORAL LOBES - Left-Handers
|
| When a left-handed person (male or female) is in constellation, for example, in a Flying Constellation, and the depression-related conflict (right temporal lobe) is stronger, the third conflict goes to the left temporal lobe because the conflict is transferred to the opposite brain hemisphere. As a result, the depression decreases and the manic mood is enhanced. The same principle applies to further conflicts.
|
|
| When a left-handed person (male or female) is in a Flying Constellation and the mania-related conflict (left temporal lobe) is stronger, the third conflict goes to the right temporal lobe because the conflict is transferred to the opposite brain hemisphere. As a result, the person is less manic and rather depressed. The same principle applies to further conflicts.
|
Further conflicts corresponding to the temporal lobes increase or decrease
a current manic or depressed mood.
PRE-MOTOR SENSORY CORTEX (Thyroid Ducts/Pharyngeal Ducts Relays)
|
| When a left-handed person (male or female) is, for example, in an Aggressive Constellation and the mania-related conflict (left temporal lobe) is stronger, the third conflict impacts in the right thyroid ducts/pharyngeal ducts relay because the conflict is transferred to the opposite brain hemisphere.
|
Further conflicts corresponding to the frontal lobe do not change
a current manic or depressed mood.
GLUCOSE CENTER
|
| When a left-handed person (male or female) is in an Aggressive Constellation and the depression-related conflict (right temporal lobe) is accentuated, the third conflict impacts in the left diencephalon because the conflict is transferred to the opposite brain hemisphere.
|
Further conflicts corresponding to the glucose center do not change
a current manic or depressed mood.
|