LUNGS
|
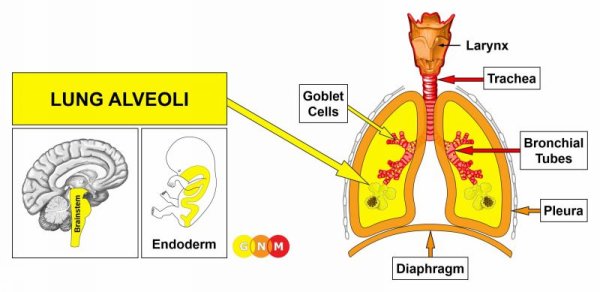
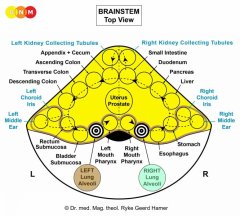
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE LUNG ALVEOLI: The lungs are located on either side of the thorax and are separated from each other by the heart. They are enclosed by the rib cage and the diaphragm, the chief muscle of respiration. The pleura protects and cushions the lungs. The function of the lungs is to deliver oxygen into the body through inhaling and to remove carbon dioxide through exhaling. After entering the nose or mouth, air travels down the trachea. The trachea divides into two bronchi that continue to split into smaller and smaller branches, called bronchioles. The bronchioles end in tiny air sacs, or lung alveoli. The alveolar cells (pneumocytes) lining the lung alveoli regulate the gas exchange between the alveoli and the blood. In evolutionary terms, the pneumocytes developed from intestinal tissue. Equal to the intestinal cells that absorb the “food morsel”, the biological function of the alveolar cells is to “absorb” (absorptive quality) the “air morsel”. The alveolar cells consist of intestinal cylinder epithelium, originate from the endoderm, and are therefore controlled from the brainstem.
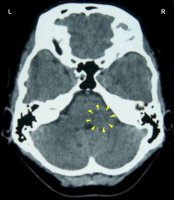
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the lung alveoli is a death-fright conflict because, in biological terms, the death panic is equated with not being able to breathe. The control center on the right side of the brainstem relates to “not being able to catch the air morsel”, that is, not being able to inhale. The control center on the left side of the brainstem relates to “not being able to eliminate the air morsel”, that is, not being able to exhale, for example, due to hyperventilation.
A death-fright can be experienced in any life-threatening situation, for example, in the course of an accident or during a medical emergency. By far the most common death-fright conflict, however, is brought on by a diagnosis shock, particularly by a cancer diagnosis that hits a person like a death sentence. Statements by a physician such as “the cancer is malignant”, “inoperable”, “aggressive”, “invasive”, “metastasizing” or remarks like “you have six months to live” and other verdicts of this kind can evoke an acute death panic. The same holds true for a negative prognosis and test results based on medical checkups (Pap tests, PSA tests, mammograms, colonoscopies, blood tests). We also have to take into account potential self-diagnosis shocks triggered, for instance, when detecting a lump, let’s say, in the breast, when there is blood in the stool, in the urine or in the vaginal discharge, or with other symptoms associated with having cancer (“a deadly disease”). Looking for information about a particular symptom on the internet with countless websites propagating the concept of “malignant diseases” can easily activate a death-fright conflict.
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: Starting with the DHS, during the conflict-active phase lung alveoli cells proliferate proportionally to the intensity of the conflict. The biological purpose of the cell increase is to improve the function of the lungs. This supplies the organism with more oxygen so that the individual is in a better position to escape from the life-threatening situation. With prolonged conflict activity (hanging conflict) flat-growing lung nodules (absorptive type), referred to as a lung cancer, develop as a result of the continuing cell augmentation (compare with “lung cancer” related to the bronchi). If the rate of cell division exceeds a certain limit, conventional medicine considers the cancer as “malignant”.
Since there are no noticeable symptoms during the conflict-active phase, lung nodules are at this point only detected through routine medical checkups or follow-up examinations. Because of today’s increased pressure for “preventive” screening and more sophisticated diagnostic tools, particularly with the invention of MRIs and mammograms, a lot more cancers are found. Consequently, many more people suffer death frights. This explains why lung cancer is still the most frequent cancer in spite of a significant decrease of the number of cigarette smokers and why even heavy smokers don’t necessarily develop lung cancer – or any cancer (see carcinogens theory).
Lung X-rays are usually performed after the diagnosis of a first cancer such as a breast cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, and others. The time-lapse between the diagnosis and further tests is, therefore, crucial because it is during this period that the lung nodules develop. Repeated follow-up exams keep the death-fright active (hanging conflict). According to Dr. Hamer, lung nodules are already visible on an X-ray after a couple of weeks following the DHS. Conventional medicine interprets the nodules as a “metastasizing cancer”. In reality, the lung cancer was caused by the death-fright over the devastating diagnosis of the first cancer resulting in a new, that is, a secondary cancer.
HEALING PHASE: Following the conflict resolution (CL), fungi or mycobacteria such as TB bacteria remove the cells that are no longer required. Healing symptoms are coughing up milky or rusty-colored phlegm. The sputum might contain blood. Because of the pus in the discharge, the symptoms might be diagnosed as purulent pneumonia or a “lung infection” (compare with pneumonia related to the bronchial mucosa). Another typical healing symptom is night sweats. If fungi assist healing, this causes lung candidiasis or a so-called “pulmonary fungal infection”.
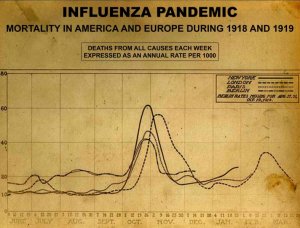
Tubercular secretion, excreted through the sputum, is rich in protein. If the healing phase is long and intense, the protein deficiency could be fatal. Death, however, is not caused by the TB-“infection” but rather by the protein depletion (for that reason, tuberculosis was formerly called “consumption”). This is exactly what happened during the lung tuberculosis epidemic of 1918/19 (see fatality statistics) after millions of people had resolved the death-fright conflicts suffered during four years of war. The end of the war initiated a mass-healing, so-to-speak, resulting in two pandemics (see also Spanish Flu). Due to the extreme poverty caused by the world economic crises that followed the First World War, those afflicted with tuberculosis did not get the protein-rich food needed for healing. Only those who could afford adequate nutrition were able to survive. The poor had no chance. Historical reports about tuberculosis epidemics claim that tuberculosis disappeared after the social and sanitary conditions had improved. In reality, it was the ensuing adequate nutrition that improved the situation. The total eradication of tuberculosis only took place where the TB bacteria were destroyed through large-scale administrations of anti-TB antibiotics, introduced in 1944. In the late 19th century, before the appearance of antibiotics, tuberculosis sanatoria provided those who were able to afford it with good nutrition together with enforced rest – a perfect setup for assisting the healing process.
Previously, the coughing up of blood (hemoptysis) was rightly diagnosed as lung tuberculosis. Today, the condition is called lung cancer (see also renaming of liver tuberculosis to liver cancer and kidney tuberculosis to “nephrotic syndrome”). It is the renaming of the disease why the numbers of lung cancer increased drastically, while tuberculosis “disappeared”, notably in the Western World where the eradication of lung tuberculosis is attributed to the “success” of extensive antibiotics regimens and vaccination (the BCG-Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine was first introduced in 1921; however, it only became widely used after the Second World War). In the “developing world”, tuberculosis is now considered a disease related to AIDS!
With water retention due to an active existence conflict involving the kidney collecting tubules, the accumulation of fluid in the lungs (in PCL-A) creates a lung edema, or alveolar edema (compare with cardiac pulmonary edema related to the myocardium and lung edema related to the mitral valve). The fluid in the lungs causes severe breathing difficulties and potentially respiratory failure (compare with water around the lungs related to the pleura). Such an acute situation typically occurs because of fear (“my life is at stake!”) or during hospitalization (see Kidney Collecting Tubule Syndrome).
After the lung nodules have been removed, caverns remain at the site. The caverns are filled with air (compare with liver caverns, pancreas caverns, breast gland caverns). With a hanging healing, that is, when healing is continuously interrupted by conflict relapses triggered by death-fright tracks, the caverns increase in size; even more so with the SYNDROME when the retained water over-inflates the caverns.
Pulmonary fibrosis is the result of recurring healing phases (compare with cystic fibrosis related to the goblet cells). In this case, the caverns are filled with fibrotic tissue. The condition is described as “scarring of the lungs”. The buildup of scar tissue is also termed pulmonary sarcoidosis, or Morbus Boeck.
If the required microbes are not available upon the resolution of the conflict, because they were destroyed through an overuse of antibiotics, the lung nodules cannot be broken down and therefore remain. Eventually, they become encapsulated. Hence, today’s excessive use of antibiotics contributes significantly to the increasing number of lung cancers that are detected during medical exams. Such encapsulated lung nodules that originated in a long-gone death-fright, might be accidentally discovered years or even decades later.
|
|
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE GOBLET CELLS: The goblet cells are single-celled glands found scattered in the bronchial mucosa and the trachea. In the bronchi, the goblet cells secrete mucus that moistens the respiratory passages and cleanses the air entering the lungs. In embryology, the goblet cells are considered residues of intestinal cells. They, therefore, consist of intestinal cylinder epithelium, originate from the endoderm and are controlled from the brainstem.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the goblet cells is a fear of suffocating, a panic of not getting enough air. The conflict could be experienced, for example, during an accident (drowning, smoke poisoning, strangulation) or a medical emergency such as an asthma attack. Newborns suffer the panic of suffocating when the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck or is cut too early, because the lungs of the newborn need a certain amount of time to get used to independent breathing. Infants have the conflict when they are put in a position where they are unable to breathe.
CONFLICT ACTIVE PHASE: In the same way as intestinal cells proliferate with a biological conflict associated with a “food morsel”, during the conflict-active phase the goblet cells increase in number in response to the distress of not getting enough air. The biological purpose of the cell proliferation is to enhance the secretion of mucus in order to better insalivate the “air morsel”. In conventional medicine, the additional cells are diagnosed as an intra-bronchial goblet cell carcinoma.
HEALING PHASE: Following the conflict resolution (CL), fungi or mycobacteria such as TB bacteria remove the cells that are no longer required. Healing symptoms are coughing up of purulent, yellow phlegm, and night sweats. With an intense healing phase, the accumulation of thick, viscous mucus in the bronchi could cause a complete clogging of the airways resulting in mucoviscidosis or cystic fibrosis with severe breathing difficulties (compare with pulmonary fibrosis related to the lung alveoli). If the healing process is prolonged (hanging healing) because of continual conflict relapses, the recurring decomposing process leads eventually to a loss of goblet cells resulting in a reduction or cessation of mucus production.
|
|
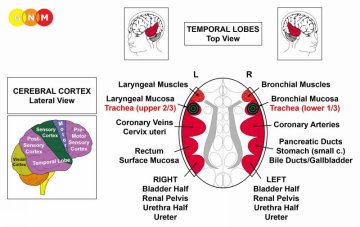
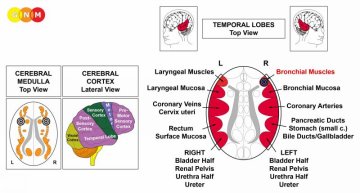
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE BRONCHIAL MUCOSA: The bronchial tubes branch from the trachea into two main bronchi from where they subdivide inside each lung into numerous small ducts, called bronchioles. The main function of the bronchi and bronchioles is to carry air into the lung alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged during respiration. The bronchial mucosa consists of squamous epithelium, originates from the ectoderm and is therefore controlled from the cerebral cortex.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the bronchial mucosa is a male territorial fear conflict or female scare-fright conflict, depending on a person’s gender, laterality, and hormone status (see also Flying Constellation). The male territorial fear conflict is the equivalent to the female nest-worry conflict. In fact, originally, Dr. Hamer termed the bronchi-related DHS a “territorial-worry conflict”.
A territorial fear conflict refers to a threat to the “territory”, a fear within the “territory” (at home, at work, at school, at the playground, in kindergarten or daycare, in a seniors home, in the hospital, or in the village, city, and country where one lives), and to a fear regarding one’s own safety as well as the safety of the “pack”. Physical abuse, family violence, mobbing, bullying, an accident, fire or flooding, an acute medical condition, a frightening diagnosis or prognosis, scary medical procedures, or hospitalization are a few examples of what can trigger the conflict. Children suffer the conflict when they are punished, abused, or yelled at, when they are terrified of a person or a situation, when they watch spooky films or videos showing monsters or vampires, or when they have nightmares. An adult’s panic can also create a territorial fear in a child! Unborn children experience the conflict in the womb when the mother is in danger or at birth during a difficult delivery. The conflict could also concern a member of the “territory” (a fear of losing a partner who secures a home or when a loved one is seriously ill, hospitalized, or diagnosed with cancer – associated with a “fatal disease”). A territorial fear can be shared by people of large regions, for example, during a natural disaster, during wartimes, or through scares of terrorist attacks or pandemic fear-mongering (AIDS, SARS, Swine Flu, and the like) by the media.
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: ulceration in the bronchial mucosa proportional to the degree and duration of conflict activity. The biological purpose of the cell loss is to widen the respiratory passageways so that more air can reach the lungs. The enhanced function of the lungs serves to facilitate a conflict resolution. There are no symptoms in the conflict-active phase.
HEALING PHASE: During the first part of the healing phase (PCL-A) the tissue loss is replenished through cell proliferation. Healing symptoms are pain due to the swelling caused by the edema (fluid accumulation), tickles in the lungs (itching or pruritus is characteristic for any healing involving squamous epithelial tissue such as the skin) and coughing. Coughing facilitates bringing up phlegm containing remnants of the repair process. Depending on the intensity of the conflict, the symptoms range from mild to severe. After the Epileptoid Crisis, in PCL-B, the swelling recedes and the function of the bronchi returns to normal.
In conventional medicine, the cell proliferation that takes place in PCL-A is diagnosed as a “lung cancer” or bronchial cancer (compare with lung cancer related to the lung alveoli). Based on the Five Biological Laws, the new cells cannot be regarded as “cancer cells” since the cell increase is, in reality, a replenishing process.
Bronchitis occurs when healing is accompanied by an inflammation, typically with fever, headaches because of the swelling in the corresponding brain relay, and fatigue since the autonomic nervous system is in a state of prolonged rest (vagotonia). In conventional medicine, recurring bronchitis is generally associated with “allergies” (see also bronchial asthma).
Pneumonia is bronchitis with the SYNDROME, that is, with water retention as a result of an active abandonment or existence conflict involving the kidney collecting tubules. In PCL-A, the retained water is exceedingly stored in the bronchial tubes (compare with lung edema). On the brain level, the excess water could lead to serious complications, particularly during the Epileptoid Crisis, which is the critical point (“pneumonic lysis”) when the brain edema is expelled. The brain pressure caused by the sympathicotonic surge could be so strong that the person falls into a coma and dies. However, if the conflict-active phase lasted less than 4-5 months, the Epi-Crisis is, according to Dr. Hamer, not life-threatening.
So-called Legionnaires’ disease is a type of pneumonia. The name originates from an outbreak of pneumonia among people who had attended a convention of the American Legion in Philadelphia in 1976. What was possibly the territorial fear conflict experienced by so many participants of the meeting?
“Bacterial pneumonia” indicates that the repair and scarring process (PCL-B) is assisted by bacteria. This is usually the case when the ulceration that takes place in the conflict-active phase reaches deep into the bronchial tissue.
Conventional medicine claims that “viral pneumonia” is caused by viruses, notably by influenza viruses that purportedly caused the Spanish Flu pandemic after the First World War or, in our days, SARS, the Bird Flu, the Swine Flu, and the like. However, none of the influenza viruses have ever been scientifically verified (details are presented in the “Virus Mania” GNM video). Threats of a global “influenza pandemic”, however, can trigger territorial fear and existence conflicts among the population resulting in a fast increase of influenza cases.
Pneumonia is also the most common lung condition associated with HIV and AIDS. As we now come to understand, there is no causal relation at all to the alleged HI-Virus but rather to a “territorial fear” or scare-fright conflict associated with the “disease”.
|
|
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE TRACHEA: The trachea or “windpipe” is a hollow tube that connects the larynx to the two bronchi of the lungs. It has the vital function of providing air flow to and from the lungs for respiration. The trachea is composed of cartilage rings, smooth muscles, and connective tissue. The tracheal mucosa lining the inner wall of the trachea consists of squamous epithelium, originates from the ectoderm and is therefore controlled from the cerebral cortex.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the trachea is not getting enough air (compare with conflict related to the diaphragm), for example, when a thyroid cyst presses onto the trachea.
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: ulceration of the tracheal lining proportional to the degree and duration of conflict activity. The biological purpose of the cell loss is to widen the trachea to get more air.
HEALING PHASE: During the first part of the healing phase (PCL-A) the tissue loss is replenished through cell proliferation. If the lower section of the trachea is affected, this causes pain behind the sternum due to the swelling and breathing difficulties. With water retention (the SYNDROME) the swelling could lead to an airway obstruction. With an inflammation, the condition is called tracheitis, typically accompanied by fever. In conventional medicine, a narrowing of the upper trachea is referred to as “Idiopathic Subglottis Stenosis”. The cell increase in the trachea might also be diagnosed as a tracheal cancer. According to GNM, the new cells cannot be regarded as “cancer cells” since the cell increase is, in reality, a replenishing process. However, a large swelling might obstruct the trachea requiring surgery to open the trachea to improve breathing.
After the Epileptoid Crisis, the edema subsides and in PCL-B the organ slowly returns to its normal function.
|
|
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE BRONCHIAL MUSCLES: The wall of the bronchi and bronchioles consists of an epithelial mucosa and a layer of smooth and striated muscles. The function of the bronchial muscles is to alter the lumen of the bronchial tubes to increase the airflow during breathing (compare with diaphragm). The striated part of the bronchial muscles originates from the new mesoderm and is controlled from the cerebral medulla and the motor cortex. NOTE: The smooth bronchial muscles are of endodermal origin and controlled from the midbrain.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the bronchial muscles is the same as for the bronchial mucosa, namely, a male territorial fear conflict or a female scare-fright conflict, depending on a person’s gender, laterality, and hormone status (see also Bronchial Asthma Constellation, Laryngeal Asthma Constellation). The distinguishing aspect of the conflict related to the muscle tissue is the additional distress of “not being able to escape”, “not being able to (re)act”, feeling “rooted to the ground” (petrified), or “feeling stuck” (see skeletal muscles).
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: cell loss (necrosis) of bronchial muscle tissue (controlled from the cerebral medulla) and, proportional to the degree of conflict activity, increasing paralysis of the bronchial muscles (controlled from the motor cortex). The paralysis causes breathing difficulties, explicitly, difficulties inhaling – exhaling is extended because of the reduced function of the bronchial muscles that control inhaling.
HEALING PHASE: During the healing phase the bronchial muscles are reconstructed. The paralysis reaches into PCL-A. The Epileptoid Crisis presents as coughing fits with bronchial spasms and convulsions, equivalent to a focal seizure (codeine-containing medication suppresses the coughing; like morphine, codeine is an opium derivative). The cough is dry, if the Biological Special Program involves only to the bronchial muscles. However, often the conflict affects both the bronchial muscles and the bronchial mucosa, which has the advantage that the combined Epileptoid Crises facilitate a faster expelling of mucus from the bronchi. This condition is referred to as “spastic bronchitis”. Whooping cough (pertussis) is also such a combined healing process (see also whooping cough related to the laryngeal muscles). In PCL-B, the function of the bronchial muscles returns to normal.
Recurring symptoms or an “allergy cough” are brought on by conflict relapses triggered by setting on a track that was established when the original conflict took place (see allergies).
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA involves two Biological Special Programs (see also laryngeal asthma)
In this case, the person is in a Bronchial Asthma Constellation, also throughout the Epileptoid Crisis which is a temporary reactivation of the conflict-active phase.
Chronic bronchial asthma attacks indicate that the related territorial fear conflict or scare-fright conflict has not been completely resolved. In conventional medicine, recurring asthma attacks are usually associated with an “allergy”.
Hence, the bronchial asthma attack involves both the striated and smooth bronchial muscles. The Epileptoid Crisis of the striated bronchial muscles presents as bronchial spasms and convulsions. The Epi-Crisis of the smooth muscles presents as a hyper-peristalsis similar to an intestinal colic. Hence, BOTH the smooth and striated bronchial muscles take part in the asthma crisis. The same applies to the laryngeal asthma attack; in this case, the smooth and striated laryngeal muscles are involved.
|
|
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE PLEURA: The pleura is a two-layered membrane that lines the lungs (visceral pleura) and the walls of the thoracic cavity (parietal pleura), including the ribs and the diaphragm. The thin space between the two pleural layers, known as the pleural cavity, is filled with serous fluid that protects the underlying tissues and allows the lungs to move easily during respiration. In evolutionary terms, the pleura developed together with the peritoneum, the pericardium, and the corium skin. The pleura originates from the old mesoderm and is therefore controlled from the cerebellum.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the pleura is an attack conflict, specifically, an attack against the chest (see also attack conflicts related to the peritoneum, pericardium, and corium skin).
An attack against the chest or torso is experienced, for instance, through a blow, stab, or hit against the chest or ribs, for example, during a fight, accident, or in sports. “Sharp” words (accusations, criticism) directed at someone or “finger pointing” could also be registered as an attack (see also pericardium). However, surgery in the chest area (removal of a tumor, mastectomy) biopsies (breast cancer biopsy), thoracoscopies, exploratory lung punctures with an insertion of a needle into a lung, tubes placed in the chest to drain fluids, or the implantation of catheters or ports into a vein of the chest for long-term intravenous treatment, including chemo treatments, also trigger attack conflicts. A lung cancer diagnosis or comments by a physician like “your lungs are not working properly” can be perceived as an “attack” regarding the integrity of the organ. Attack conflicts also originate from inside the chest, for instance, with chest pain caused by coughing (pneumonia, bronchial asthma) or stabbing and piercing pain through the inhalation of fumes, gases, or volatile liquids.
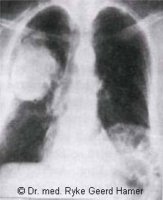
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: Starting with the DHS, during the conflict-active phase pleural cells proliferate proportionally to the intensity of the conflict. The biological purpose of the cell increase is to create an internal reinforcement to protect the chest against further attacks. With prolonged conflict activity a bulb-shaped growth forms at the site; cell augmentation on a flat plane usually occurs when the attack conflict was more of a general nature. In conventional medicine, the thickening of the pleura is diagnosed as a pleural mesothelioma (see also peritoneal mesothelioma, omental mesothelioma, pericardial mesothelioma, and testicular mesothelioma). If the rate of cell division exceeds a certain limit, then the cancer is considered “malignant”.
Since there are no symptoms during the conflict-active phase, a pleural mesothelioma is usually only found through routine medical examinations, notably among asbestos workers who have to undergo regular lung check-ups.
HEALING PHASE: Following the conflict resolution (CL), fungi, mycobacteria or other bacteria remove the cells that are no longer needed. Healing symptoms are chest pain, painful coughing, breathing difficulties, fever, and night sweats. If the required microbes are not available upon the resolution of the conflict, because they were destroyed through an overuse of antibiotics, the additional cells remain. Eventually, the growth becomes encapsulated with connective tissue. Now, the mesothelioma is regarded as “benign”.
Pleurisy or pleuritis indicates that healing is accompanied by an inflammation – with fever, if the healing phase is intense. During the healing process (in PCL-A), the fluid in the pleural cavety is naturally absorbed by the pleural membrane (dry pleurisy). Water retention, however, due to an active abandonment or existence conflict, increases the fluid accumulation (wet pleurisy) causing acute breathing difficulties; if bacteria assist healing, the fluid contains pus (purulent pleurisy). Wet pleurisy often develops during hospitalization, after surgery in the breast or chest area, or following a lung cancer or pleural mesothelioma diagnosis.
With the SYNDROME the retained water generates an exudative pleural effusion (excess fluid around the lungs as opposed to water in the lungs with pneumonia or a lung edema). Since the right and left pleura are separate from each other, the effusion occurs only on the affected side (compare with peritoneal effusion and pericardial effusion). A pleural effusion could cause serious complications, particularly when the fluid-filled pleural cavity compresses both lungs. In this case, a pleural puncture to drain the pleural cavety is unavoidable.
Pleural fluid is rich in protein. Hence, constant draining of the extra fluid leads to protein deficiency and rapid weight loss. Furthermore, the pleural punctures trigger often new attack conflicts and conflict relapses with each procedure (hospital “track”), throwing the person into a vicious cycle. Puncturing the pleura also bears the risk of a lung collapse or pneumothorax (see also pneumothorax and lung emphysema).
|
|
DEVELOPMENT AND FUNCTION OF THE DIAPHRAGM: The diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen. It is the largest and most efficient muscle used in breathing. During inhaling, the diaphragm moves down, the lungs expand and air is drawn in; during exhaling, the diaphragm relaxes and air leaves the lungs (compare with bronchial muscles). In addition to breathing, the contraction of the diaphragm supports the heart muscle (myocardium) in sucking venous blood from the systemic circulation. For this, the left half of the diaphragm is of greater importance since the right half has less ability to move due to the liver positioned directly underneath. The diaphragm consists of striated muscles, originates from the new mesoderm and is controlled from the cerebral medulla and the motor cortex. For its involuntary supportive functions pertaining to breathing and circulation, the diaphragm also receives impulses from the brainstem.
BIOLOGICAL CONFLICT: The biological conflict linked to the diaphragm is not being able to breathe sufficiently or deeply enough, for example, when getting out of breath during hard exercises such as jogging (sprinting) or when running too fast (catching a bus, escaping from danger). An unexpected shock (“it took my breath away”), fright or scare (see also scare-fright conflict) can cause this type of breathing conflict (see also trachea). Feeling physically overwhelmed (excessive physical demands or not being able to handle the distress, for example, with a partner, child, or parent physically) also affects the diaphragm (compare with emotional and mental overwhelmed conflict related to the myocardium). Coupled with the myocardium, the conflict is experienced as running out of breath because “This is too much!”
CONFLICT-ACTIVE PHASE: cell loss (necrosis) of diaphragm muscle tissue (controlled from the cerebral medulla) and, proportional to the degree of conflict activity, increasing paralysis of the diaphragm muscle (controlled from the motor cortex) causing difficulties breathing ranging from mild to severe. Lasting paralysis results in an elevated hemidiaphragm.
With lasting, intense conflict activity the ongoing tissue loss can lead to a rupture of the diaphragm (diaphragmatic hernia) with abdominal organs moving into the chest cavity. In case of a hiatal hernia, the weakened diaphragm muscle allows a small part of the stomach to bulge up through the diaphragm and into the chest (compare with inguinal hernia). The rupture could be brought on by coughing, heavy lifting, pulling or pushing, or pressing too hard, for example, during a bowel movement.
HEALING PHASE: In the healing phase, the diaphragm muscle is reconstructed. The partial paralysis reaches into PCL-A. The Epileptoid Crisis presents as cramping or spasms of the diaphragm accompanied by breathing difficulties. Sleep apnea with episodes of cessation of breathing is generated by the contractions of the diaphragm during the Epi-Crisis. Chronic sleep apnea points to conflict relapses (compare with sleep apnea related to the myocardium).
Stitches in the side, for example, when exercising shortly after eating, running too fast or talking during jogging, is a manifestation of a small diaphragm-related Epileptoid Crisis. Hiccups (singultus) are diaphragmatic contractions or flutters, typically caused by eating or drinking too quickly without adequate breathing. In this case, the “conflict” is solely of a biological nature without an emotional component. However, persisting hiccups that last longer than 48 hours are caused by breathing conflict.
|