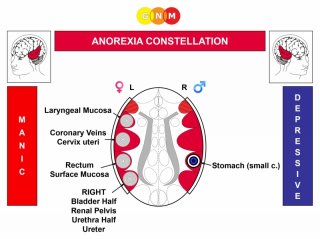
Anorexia Constellation
ANOREXIA CONSTELLATION
Biological conflicts: territorial anger conflict or identity conflict and any conflict that corresponds to the left temporal lobe (scare-fright conflict, sexual conflict, a second identity conflict, or a marking conflict). The conflict sequence is determined by gender, laterality, and hormone status.
Brain and Organ Level: The corresponding brain relays are the control centers of the small curvature of the stomach (right temporal lobe) and the laryngeal mucosa, cervix uteri/coronary veins, the rectum surface mucosa, or bladder/urethra/ureter/renal pelvis (left temporal lobe).
Once the second conflict occurs, the person is in constellation and manic-depressive (compare with primary mania and primary depression). Whether the manic or depressed mood is dominant is determined by which of the two conflicts is stronger. The constellation can be permanent or recurring due to tracks or conflict relapses.
Anorexia (anorexia nervosa) presents as compulsive fasting and a refusal to eat. Anorexics might weigh themselves several times a day. The fear of gaining weight is the main conflict track. A prolonged Anorexia Constellation causes extreme weight loss and can, therefore, be life-threatening.
Like with bulimia, the onset of anorexia occurs most commonly in young women in their teenage years. Young girls and adolescents are particularly susceptible to suffer conflicts associated with their weight because at this age they are more vulnerable concerning their looks. However, girls as young as 8 years have also become anorexic as well as women in their sixties. Boys and adult males have anorexia too.
Mental manifestation:
|